Google is updating its algorithm to consider copyright infringement claims against webpages as a signal to lower a site’s rankings. They already have more than 200 signals used in ranking results. This new signal is based on, “the number of valid copyright removal notices we receive for any given site. Sites with high numbers of removal notices may appear lower in our results.”
What Data is Used?
DMCA is the Digital Millennium Copyright Act enacted in 1998 that, among other things, addresses U.S. Copyright laws related to the internet. Per Google’s FAQ:
The DMCA or Digital Millennium Copyright Act is a U.S. law that provides qualifying online service providers like Google with a safe harbor from monetary liability for copyright infringement claims. One of the requirements of these safe harbor provisions is that the service provider remove or disable access to allegedly infringing material upon receiving a request that meets certain requirements. In responding to copyright removal requests, Google complies with the requirements of the DMCA.
This means that Google has direct access to claims of copyright infringement through their own copyright removal requests process. By incorporating this information into their algorithm, they can push repeat reported offenders’ sites further down the ranking in the search results pages.
Why it Matters
There’s plenty of controversy surrounding this update, but for small businesses marketing online some of the takeaways are:
- Yet another reminder that algorithm changes constantly
- It makes sense that Google will try to keep the search results relevant using all means at their disposal, consider that with everything you do online
- Don’t infringe on copyrights
- If someone makes a false copyright takedown request against you, respond to it
- Monitor for yourself if a copyright removal requests is made against you
A few more relevant Google Removal FAQs:
How quickly do you remove search results after a request is made?
We remove search results that link to infringing content in Search when it is brought to our attention, and we do it quickly. As of May 2012, our average processing time across all removal requests submitted via our web form for Search is approximately 10 hours. However, many different factors can influence the processing time for a particular removal request, including the method of delivery, language, and completeness of the information submitted.
How many of these requests did you comply with?
We removed 97% of search results specified in requests that we received between July and December 2011.
Do you inform users before acting on a request?
When feasible and legal to do so, we try our best to notify users to give them an opportunity to submit a counter-notice in response to copyright removal requests. For Search, it is extremely difficult to provide meaningful notice to webmasters whose pages have been identified in copyright removal requests, because we do not necessarily know their identities or have an effective means of contacting them. If users have registered with our Webmaster Tools as web site owners, we will notify them there. We also share a copy of qualifying copyright removal requests with the public site Chilling Effects, where a webmaster may inspect it as well.
Why Now?
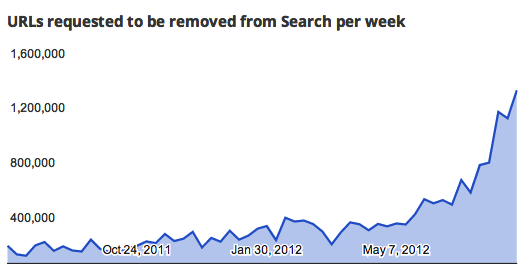
As seen in Google’s graph below of URLs requested to be removed from Search per week, the increase in the number of copyright removal notices is significant, and according to them now provides enough data to use in their algorithm:
Per Google in their announcement:
Since we re-booted our copyright removals over two years ago, we’ve been given much more data by copyright owners about infringing content online. In fact, we’re now receiving and processing more copyright removal notices every day than we did in all of 2009…we will now be using this data as a signal in our search rankings.